For all recorded transactions, if the total debits and credits for a transaction are equal, then the result is that the company’s assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and equity. If a business buys raw materials and pays in cash, it will result in an increase in the company’s inventory (an asset) while reducing cash capital (another asset). Because there startup checklist a comprehensive list are two or more accounts affected by every transaction carried out by a company, the accounting system is referred to as double-entry accounting. This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is considered to be the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. The accounting equation ensures that the balance sheet remains balanced.
- The capital would ultimately belong to you as the business owner.
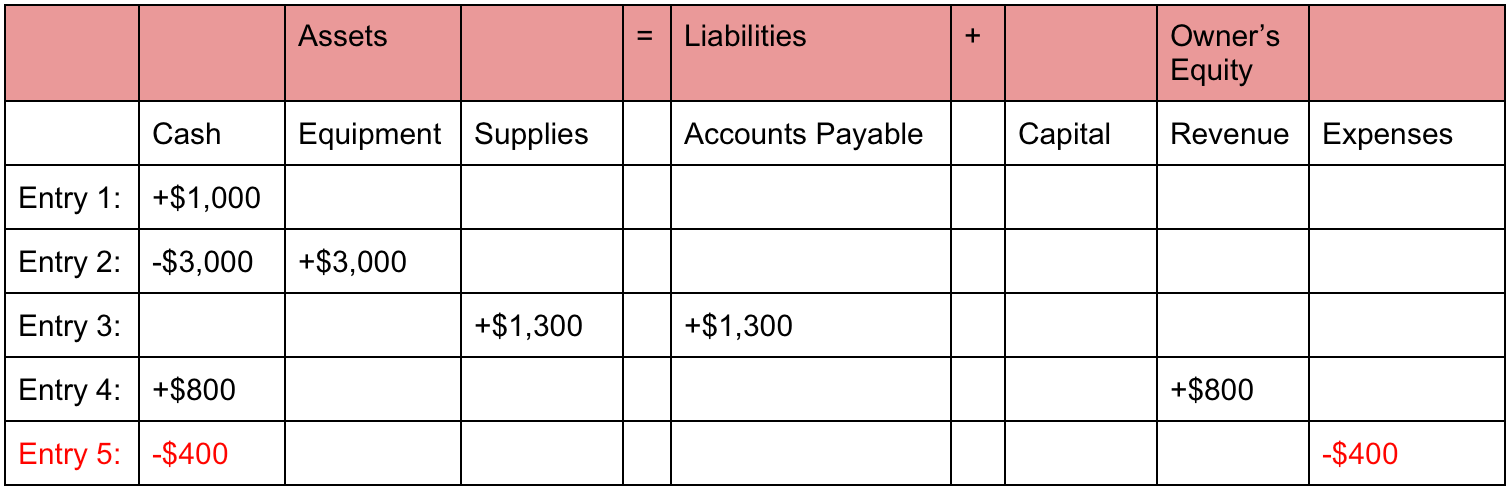
- On 1 January 2016, Sam started a trading business called Sam Enterprises with an initial investment of $100,000.
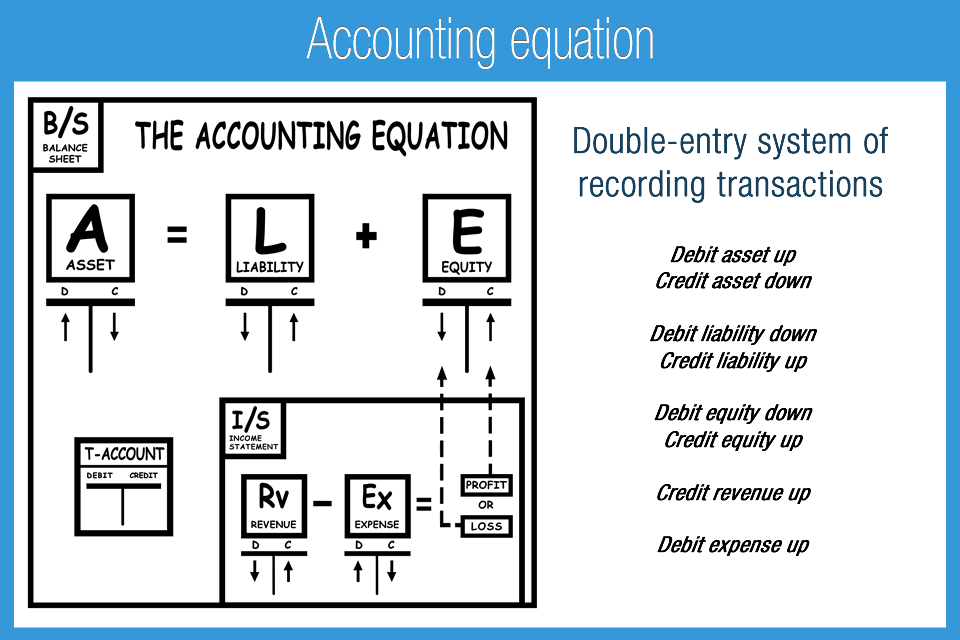
- The accounting equation states that total assets is equal to total liabilities plus capital.
- The effect of this transaction on the accounting equation is the same as that of loss by fire that occurred on January 20.
- The accounting equation states that a company’s assets must be equal to the sum of its liabilities and equity on the balance sheet, at all times.
Financial statements
On 12 January, Sam Enterprises pays $10,000 cash to its accounts payable. This transaction would reduce an asset (cash) and a liability (accounts payable). Creditors have preferential rights over the assets of the business, and so it is appropriate to place liabilities before the capital or owner’s equity in the equation. While single-entry accounting can help you kickstart your bookkeeping knowledge, it’s a dated process that many other business owners, investors, and banks won’t rely on.
Basic Accounting Equation Formula
11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. The merchandise would decrease by $5,500 and owner’s equity would also decrease by the same amount.
Which three components make up the Accounting Equation?
As inventory (asset) has now been sold, it must be removed from the accounting records and a cost of sales (expense) figure recorded. The cost of this sale will be the cost of the 10 units of inventory sold which is $250 (10 units x $25). The difference between the $400 income and $250 cost of sales represents a profit of $150. The inventory (asset) will decrease by $250 and a cost of sale (expense) will be recorded.
The accounting equation ensures the balance sheet is balanced, which means the company is recording transactions accurately. Accounting equation describes that the total value of assets of a business entity is always equal to its liabilities plus owner’s equity. This equation is the foundation of modern double entry system of accounting being used by small proprietors to large multinational corporations. Other names used for this equation are balance sheet equation and fundamental or basic accounting equation. The accounting equation is the backbone of the accounting and reporting system.
The income statement is also referred to as the profit and loss statement, P&L, statement of income, and the statement of operations. The income statement reports the revenues, gains, expenses, losses, net income and other totals for the period of time shown in the heading of the statement. If a company’s stock is publicly traded, earnings per share must appear on the face of the income statement. The owner’s equity is the balancing amount in the accounting equation. So whatever the worth of assets and liabilities of a business are, the owners’ equity will always be the remaining amount (total assets MINUS total liabilities) that keeps the accounting equation in balance. The purpose of this article is to consider the fundamentals of the accounting equation and to demonstrate how it works when applied to various transactions.
All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. On 22 January, Sam Enterprises pays $9,500 cash to creditors and receives a cash discount of $500. The difference between the sale price and the cost of merchandise is the profit of the business that would increase the owner’s equity by $1,000 (6,000 – $5,000).

Every transaction is recorded twice so that the debit is balanced by a credit. As you can see, all of these transactions always balance out the accounting equation. This equation holds true for all business activities and transactions. If assets increase, either liabilities or owner’s equity must increase to balance out the equation.
However, due to the fact that accounting is kept on a historical basis, the equity is typically not the net worth of the organization. Often, a company may depreciate capital assets in 5–7 years, meaning that the assets will show on the books as less than their “real” value, or what they would be worth on the secondary market. If a transaction is completely omitted from the accounting books, it will not unbalance the accounting equation. The accounting equation shows the amount of resources available to a business on the left side (Assets) and those who have a claim on those resources on the right side (Liabilities + Equity). Metro Courier, Inc., was organized as a corporation on January 1, the company issued shares (10,000 shares at $3 each) of common stock for $30,000 cash to Ron Chaney, his wife, and their son. The company acquired printers, hence, an increase in assets.
The expanded accounting equation is derived from the common accounting equation and illustrates in greater detail the different components of stockholders’ equity in a company. The fundamental accounting equation, also called the balance sheet equation, is the foundation for the double-entry bookkeeping system and the cornerstone of accounting science. In the accounting equation, every transaction will have a debit and credit entry, and the total debits (left side) will equal the total credits (right side). In other words, the accounting equation will always be “in balance”.
If a company’s assets were hypothetically liquidated (i.e. the difference between assets and liabilities), the remaining value is the shareholders’ equity account. Although the balance sheet always balances out, the accounting equation can’t tell investors how well a company is performing. The accounting equation is also called the basic accounting equation or the balance sheet equation. Substituting for the appropriate terms of the expanded accounting equation, these figures add up to the total declared assets for Apple, Inc., which are worth $329,840 million U.S. dollars.