They were acquired by borrowing money from lenders, receiving cash from owners and shareholders or offering goods or services. The assets of the business will increase by $12,000 as a result of acquiring the van (asset) but will also decrease by an equal amount due to the payment of cash (asset). We will now consider an example with various transactions within a business to see how each has a dual aspect and to demonstrate the cumulative effect on the accounting equation.
Company
Metro Courier, Inc., was organized as a corporation on January 1, the company issued shares (10,000 shares at $3 each) of common stock for $30,000 cash to Ron Chaney, his wife, and their son. The travel agency accounting is similar to the format of the balance sheet. On 10 January, Sam Enterprises sells merchandise for $10,000 cash and earns a profit of $1,000. As a result of this transaction, an asset (i.e., cash) increases by $10,000 while another asset ( i.e., merchandise) decreases by $9,000 (the original cost). Creditors have preferential rights over the assets of the business, and so it is appropriate to place liabilities before the capital or owner’s equity in the equation. There are different categories of business assets including long-term assets, capital assets, investments and tangible assets.
What Are the 3 Elements of the Accounting Equation?
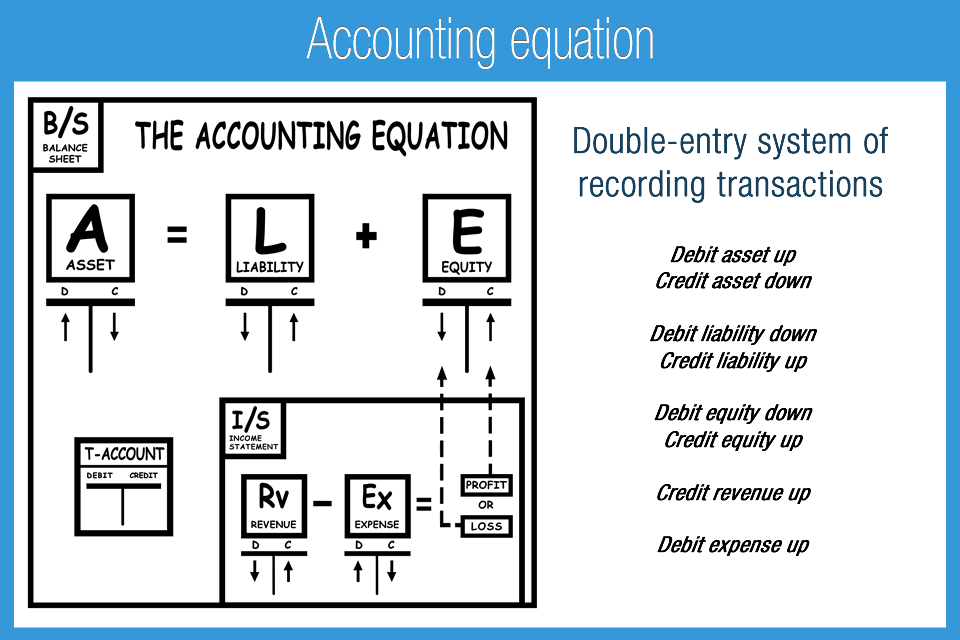
Accounting equation describes that the total value of assets of a business entity is always equal to its liabilities plus owner’s equity. This equation is the foundation of modern double entry system of accounting being used by small proprietors to large multinational corporations. Other names used for this equation are balance sheet equation and fundamental or basic accounting equation. Examples of assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid insurance, investments, land, buildings, equipment, and goodwill.
What Are the Three Elements in the Accounting Equation Formula?
- It can also cause problems with taxes and audits, as well as customers who may suspect fraud or mishandling of funds as a result of an unbalanced equation.
- The impact of this transaction is a decrease in an asset (i.e., cash) and an addition of another asset (i.e., building).
- Assets entail probable future economic benefits to the owner.
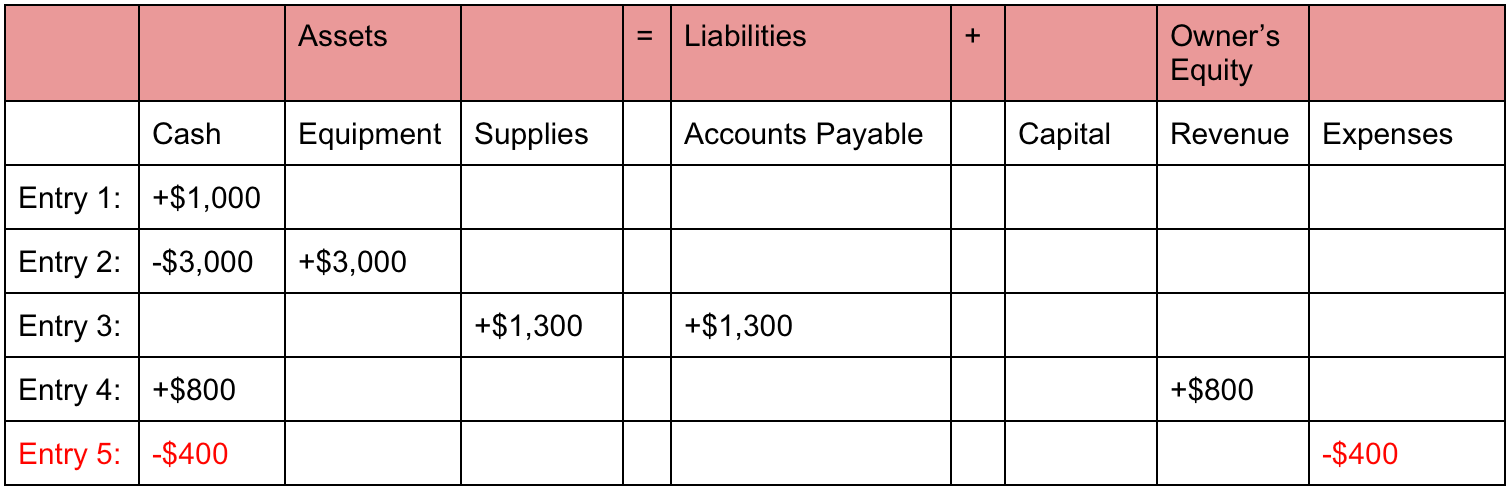
- To further illustrate the analysis of transactions and their effects on the basic accounting equation, we will analyze the activities of Metro Courier, Inc., a fictitious corporation.
- The accounting equation is fundamental to the double-entry bookkeeping practice.
Capital essentially represents how much the owners have invested into the business along with any accumulated retained profits or losses. The capital would ultimately belong to you as the business owner. This is how the accounting equation of Laura’s business looks like after incorporating the effects of all transactions at the end of month 1.
Owners’ Equity
These are fixed assets that are usually held for many years. Assets include cash and cash equivalents or liquid assets, which may include Treasury bills and certificates of deposit (CDs). However, this scenario is extremely rare because every transaction always has a corresponding entry on each side of the equation.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
The assets have been decreased by $696 but liabilities have decreased by $969 which must have caused the accounting equation to go out of balance. To calculate the accounting equation, we first need to work out the amounts of each asset, liability, and equity in Laura’s business. Like any brand new business, it has no assets, liabilities, or equity at the start, which means that its accounting equation will have zero on both sides. Essentially, the representation equates all uses of capital (assets) to all sources of capital, where debt capital leads to liabilities and equity capital leads to shareholders’ equity. Equity refers to the owner’s interest in the business or their claims on assets after all liabilities are subtracted.
Additionally, you can use your cover letter to detail other experiences you have with the accounting equation. For example, you can talk about a time you balanced the books for a friend or family member’s small business. The accounting equation will always remain in balance if the double entry system of accounting is followed accurately.
The accounting equation states that total assets is equal to total liabilities plus capital. This lesson presented the basic accounting equation and how it stays equal. The income and retained earnings of the accounting equation is also an essential component in computing, understanding, and analyzing a firm’s income statement. This statement reflects profits and losses that are themselves determined by the calculations that make up the basic accounting equation. In other words, this equation allows businesses to determine revenue as well as prepare a statement of retained earnings.
That part of the accounting system which contains the balance sheet and income statement accounts used for recording transactions. In our examples below, we show how a given transaction affects the accounting equation. We also show how the same transaction affects specific accounts by providing the journal entry that is used to record the transaction in the company’s general ledger. Although the balance sheet always balances out, the accounting equation can’t tell investors how well a company is performing.
Both liabilities and shareholders’ equity represent how the assets of a company are financed. If it’s financed through debt, it’ll show as a liability, but if it’s financed through issuing equity shares to investors, it’ll show in shareholders’ equity. It is important to remember that the total of all assets has to equal the total of liabilities and equity. This is what ensures that every transaction makes sense and there will always be an entry on both sides of each transaction. Accountants and members of a company’s financial team are the primary users of the accounting equation. Understanding how to use the formula is a crucial skill for accountants because it’s a quick way to check the accuracy of transaction records .
It is based on the idea that each transaction has an equal effect. It is used to transfer totals from books of prime entry into the nominal ledger. Every transaction is recorded twice so that the debit is balanced by a credit. For a company keeping accurate accounts, every business transaction will be represented in at least two of its accounts. For instance, if a business takes a loan from a bank, the borrowed money will be reflected in its balance sheet as both an increase in the company’s assets and an increase in its loan liability.