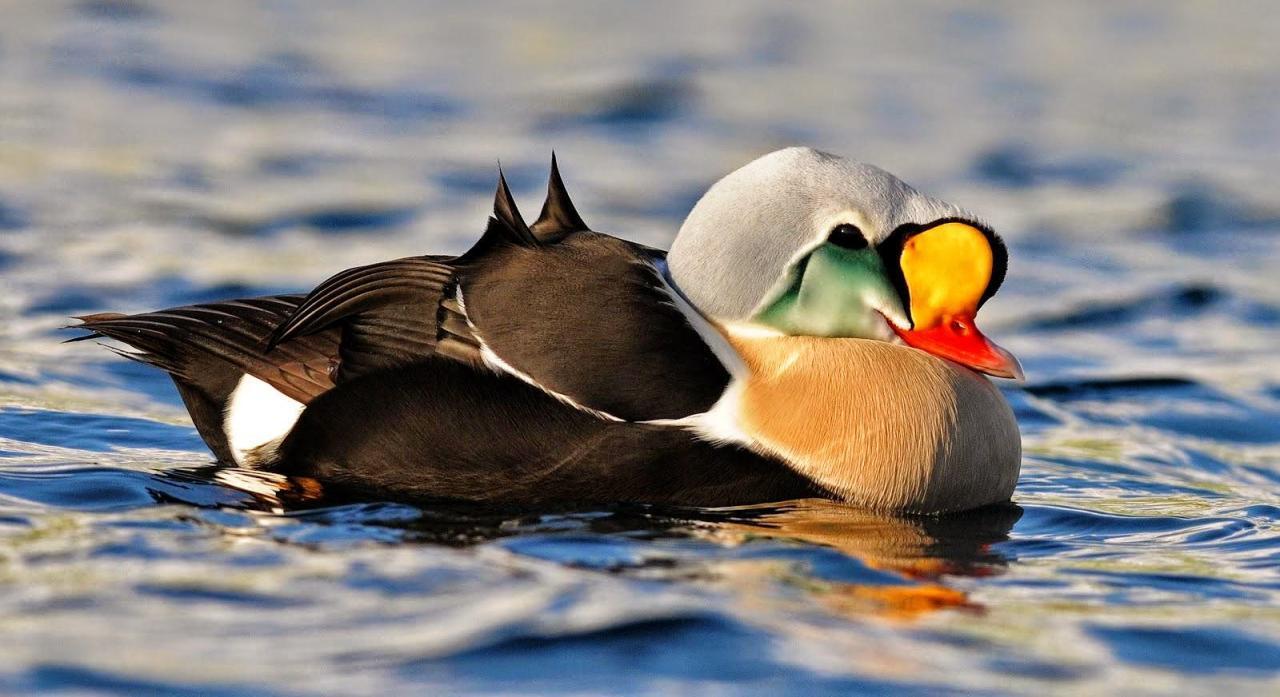

Native to the coastal tundras of Alaska and northeastern Siberia, the Spectacled Eider’s breeding habitat is as harsh as it is remote. These birds prefer moist coastal areas and nest in tundra grasses, where they can remain relatively undisturbed by predators and human activity. During the winter, they migrate to the Bering Sea, forming large, dense flocks that float on the icy waters, sometimes in rafts numbering in the tens of thousands.
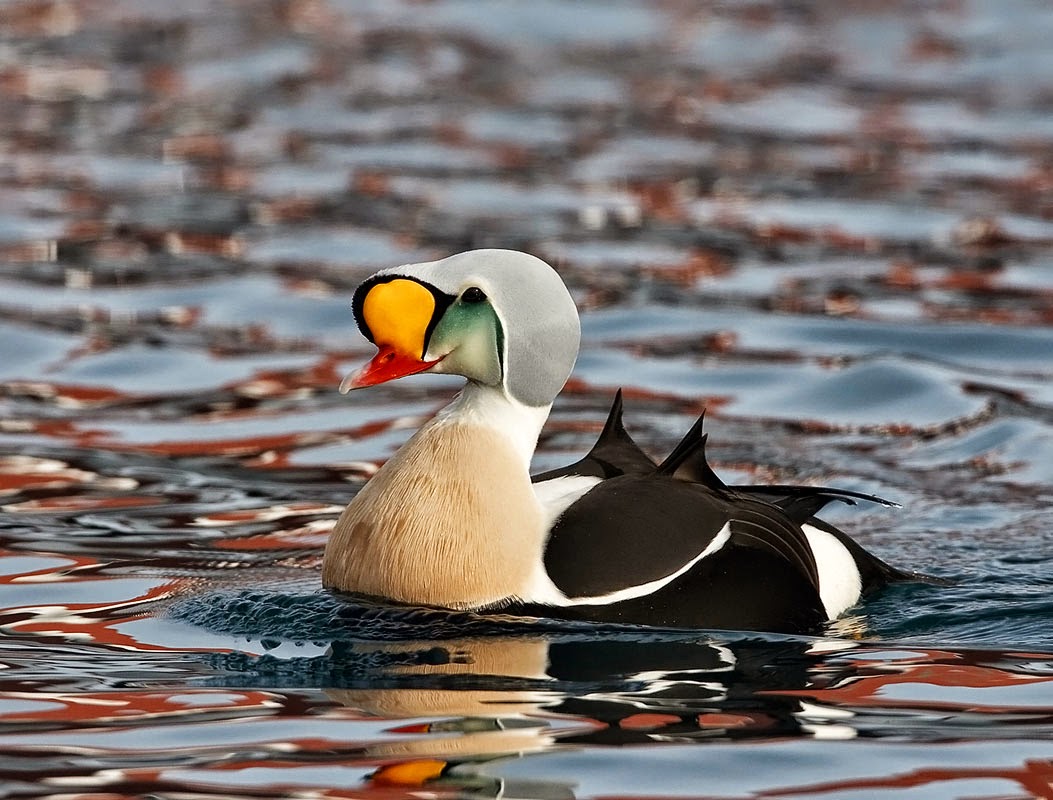

The plumage of the Spectacled Eider is a study in contrast. Males sport a striking combination of black and white with a greenish hue on the head, while females are cloaked in a mottled brown coat, providing camouflage against the tundra. Both sexes share the characteristic white eye patches, which give them their “glasses” name and almost whimsical appearance.
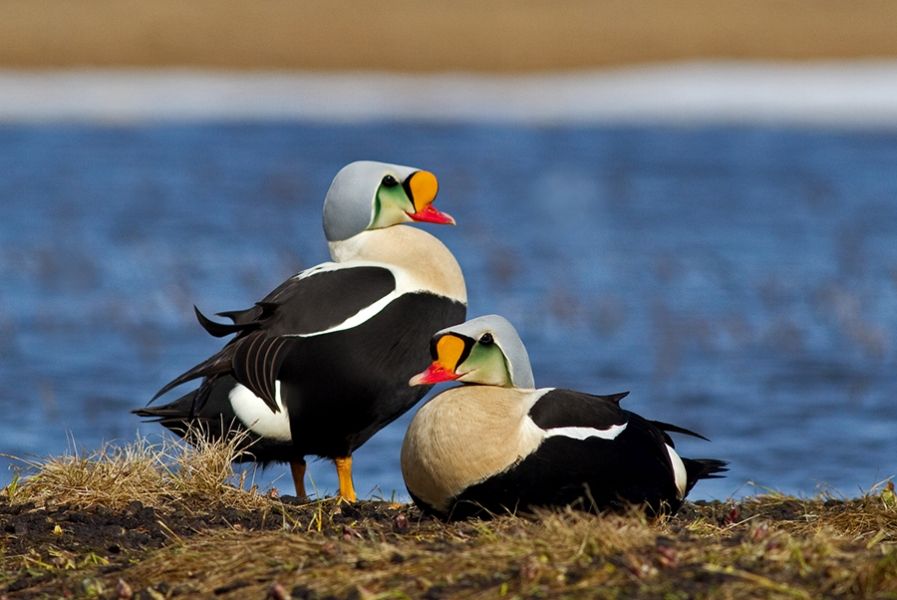

Despite their captivating appearance, spectacled eiders face significant challenges. Their populations have experienced declines due to habitat alteration, climate change, and increased predation. Conservation efforts are underway to monitor their populations and protect their habitats. These efforts are critical, as the species’ unique life history traits make it particularly vulnerable to environmental changes.
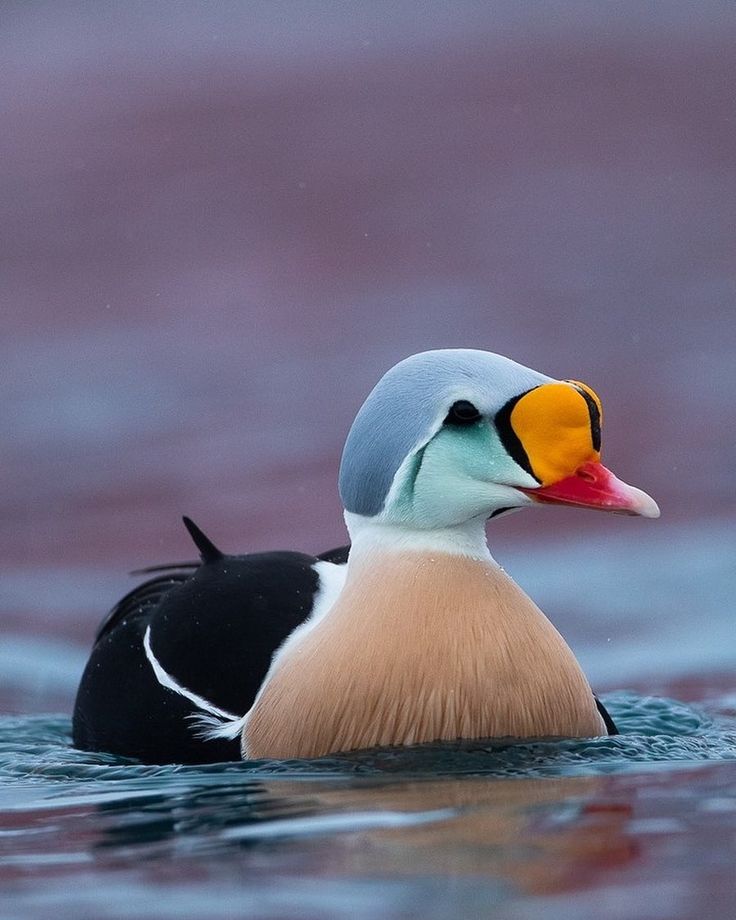

The Spectacled Eider’s diet is as fascinating as its appearance. They dive to the seabed to search for food, feeding on mollusks, crustaceans and other invertebrates. This diving ability, combined with its specialized beak designed to catch prey, highlights its adaptation to the demanding Arctic environment.
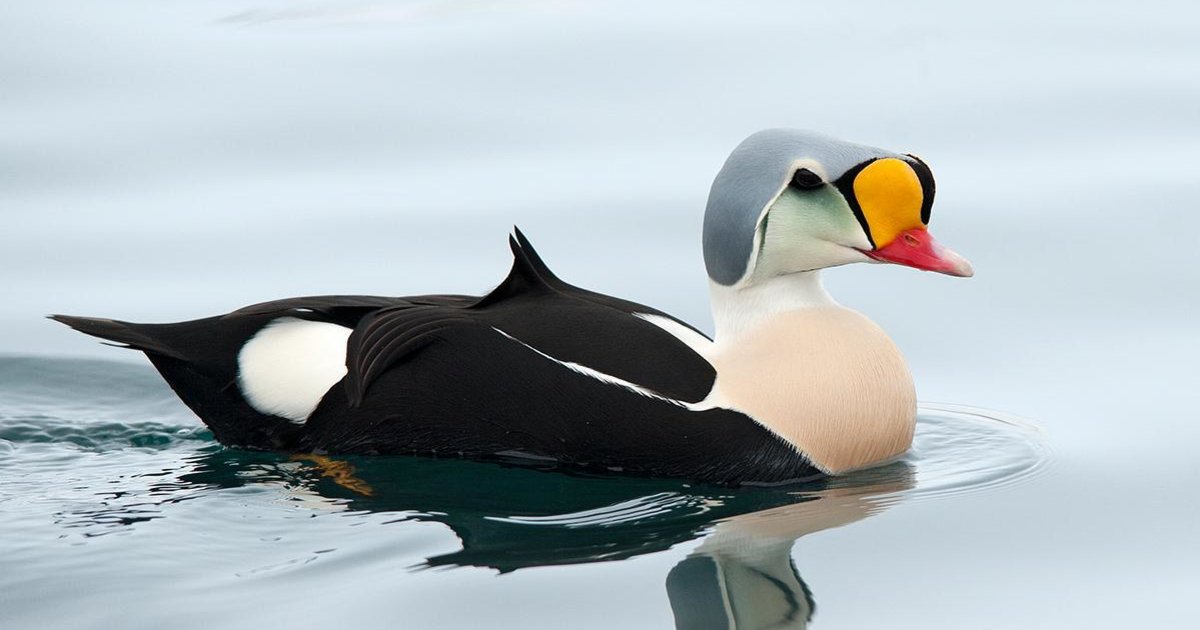

Observing a spectacled eider in its natural habitat is a rare privilege, often reserved for those who venture to the remote corners of the Arctic. For many, the sight of this rare and beautifully adapted bird is a reminder of the planet’s rich biodiversity and the importance of protecting these extraordinary species.
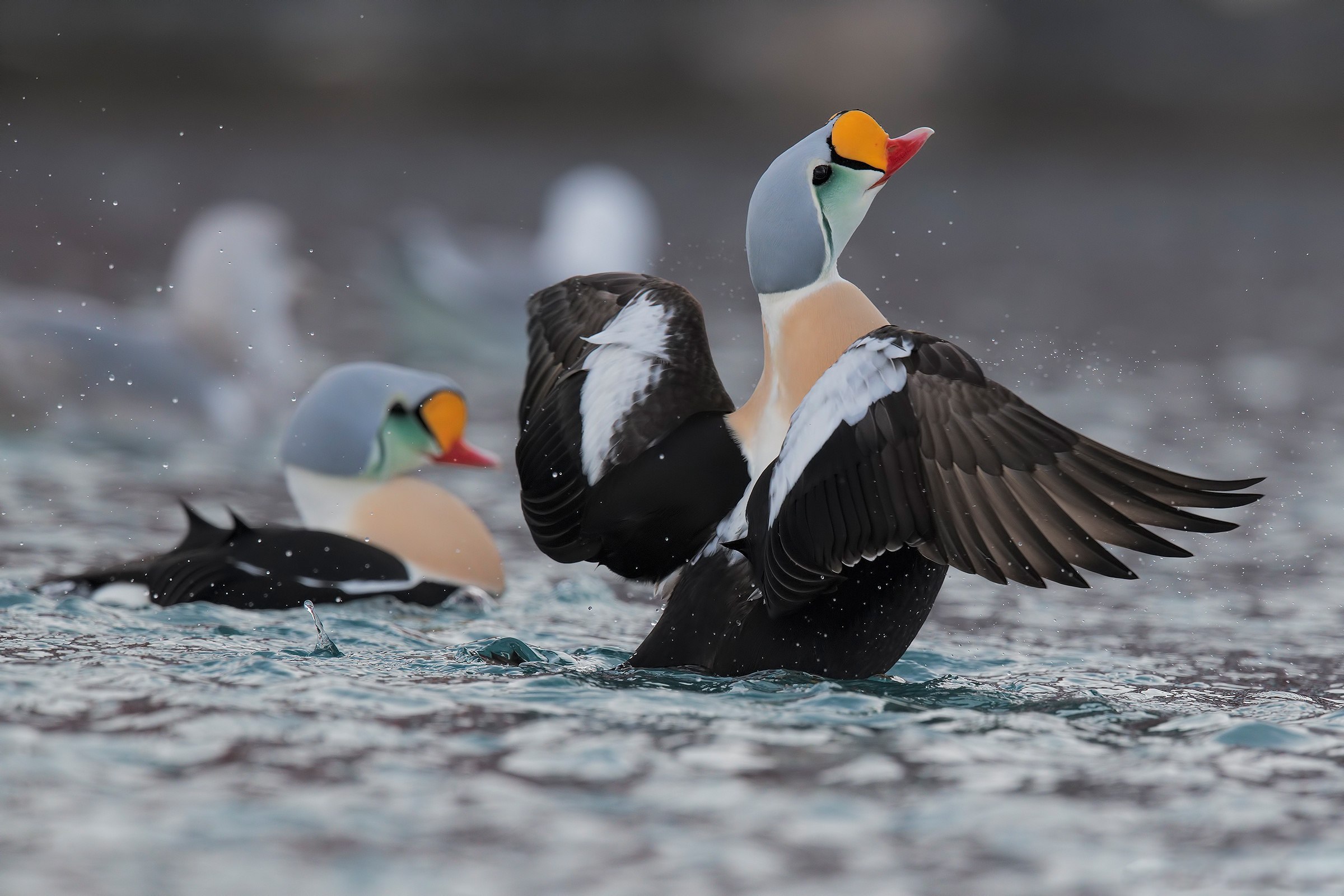
In conclusion, the Spectacled Eider is more than just a captivating waterfowl; It is a symbol of the resilience and adaptability of wildlife in one of the most extreme environments on the planet. Its unique appearance and intriguing lifestyle continue to fascinate scientists and bird watchers, underscoring the urgent need for conservation efforts to ensure that future generations can also marvel at this extraordinary species.





